Index
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
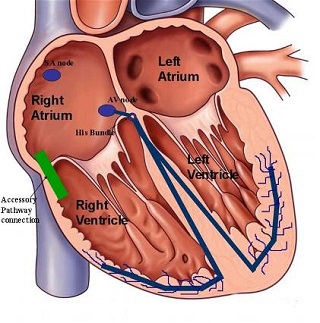
What Is Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Defect?
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome [WPWS] is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart which has resulted in symptoms.
About 40% of people with the electrical problem never develop symptoms.
What Causes Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Defect?
The cause of Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome [WPW] is typically unknown. A small number of cases are due to a mutation of the PRKAG2 gene which may be inherited
from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant fashion. The underlying mechanism involves an accessory electrical conduction pathway
between the atria and the ventricles. It is associated with other conditions such as Ebstein anomaly and hypokalemic periodic paralysis.

What are the Signs & Symptoms of Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Defect?
Symptoms can include an abnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or syncope.
Rarely, cardiac arrest may occur.
The most common type of irregular heartbeat that occurs is known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Rarely, cardiac arrest may occur.
The most common type of irregular heartbeat that occurs is known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
HEART CONDITIONS Diseases and Treated FAQ's
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome [WPW] is commonly diagnosed on the basis of the electrocardiogram in an asymptomatic individual.
In this case, it is manifested as a delta wave, which is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex that is associated with a short PR interval. The short PR interval and slurring of the QRS complex are reflective of the impulse making it to the ventricles early (via the accessory pathway) without the usual delay experienced in the AV node.
In this case, it is manifested as a delta wave, which is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex that is associated with a short PR interval. The short PR interval and slurring of the QRS complex are reflective of the impulse making it to the ventricles early (via the accessory pathway) without the usual delay experienced in the AV node.
People with Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome [WPW] who are experiencing tachydysrhythmias may require synchronized
electrical cardioversion if they are demonstrating severe signs or symptoms (for example, low blood pressure or lethargy with altered mental status).
If they are relatively stable, medication may be used.
Also can be use some medications.
Radiofrequency catheter ablation.
If they are relatively stable, medication may be used.
Also can be use some medications.
Radiofrequency catheter ablation.