Index
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
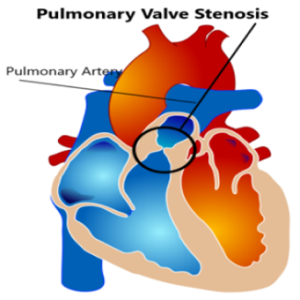
What Is Pulmonary Valve Stenosis?
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes
through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve
stenosis this opening is too narrow, leading to a reduction of flow of blood to the lungs.
While the most common cause of pulmonary valve stenosis is congenital heart disease, it may also be due to
a malignant carcinoid tumor. Both stenosis of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve stenosis are forms of
pulmonic stenosis (nonvalvular and valvular, respectively) but pulmonary valve stenosis accounts for 80% of
pulmonic stenosis. PVS was the key finding that led Jacqueline Noonan to identify the syndrome now called Noonan syndrome.
What Causes Pulmonary Valve Stenosis?
In regard to the cause of pulmonary valve stenosis higher percentage are congenital, the right ventricular flow is hindered (or obstructed by this).
The cause in turn is divided into:
- Valvular External, and
- Intrinsic (when it is acquired).
The cause in turn is divided into:
- Valvular External, and
- Intrinsic (when it is acquired).

What are the Signs & Symptoms of Pulmonary Valve Stenosis?
Among some of the symptoms consistent with pulmonary valve stenosis are the following:
Heart Murmur, / Cyanosis, / Dyspnea, / Dizziness, / Upper thorax pain, and / Developmental disorders.
Heart Murmur, / Cyanosis, / Dyspnea, / Dizziness, / Upper thorax pain, and / Developmental disorders.
HEART CONDITIONS Diseases and Treated FAQ's
The diagnosis of pulmonary valve stenosis can be achieved via echocardiogram, as well as a
variety of other means among them are: ultrasound, in which images of the heart chambers in utero where
the tricuspid valve has thickening (or due to Fallot's tetralogy, Noonan's syndrome, and other congenital defects)
and in infancy auscultation of the heart can reveal identification of a murmur.
Some other conditions to contemplate (in diagnosis of pulmonic valvular stenosis) are the following:
- Infundibular Stenosis,
- Supravalvular Pulmonary Stenosis,
- Dysplastic Pulmonic Valve Stenosis.
- Infundibular Stenosis,
- Supravalvular Pulmonary Stenosis,
- Dysplastic Pulmonic Valve Stenosis.
In terms of treatment for pulmonary valve stenosis, valve replacement or surgical repair
(depending upon whether the stenosis is in the valve or vessel) may be indicated. If the valve stenosis is
of congenital origin, balloon valvuloplasty is another option, depending on the case. Valves made from animal
or human tissue (are used for valve replacement), in adults metal valves can be used.