Index
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
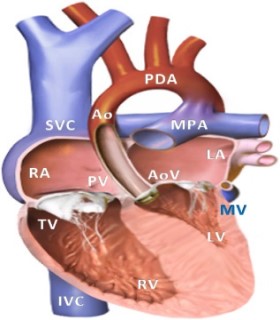
What Is Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome?
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a rare congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped.
It may affect the left ventricle, aorta, aortic valve, or mitral valve.
What Causes Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome?
There is no known cause in the majority of HLHS cases.
Some cases may have a genetic component, as HLHS has been shown to be heritable and associated with specific gene mutations.
Not all, but some, cases of aortic stenosis in a fetus can put stress on the left ventricle in utero, that can eventually lead to decreased perfusion and stop the growth of the left ventricle.
Some cases may have a genetic component, as HLHS has been shown to be heritable and associated with specific gene mutations.
Not all, but some, cases of aortic stenosis in a fetus can put stress on the left ventricle in utero, that can eventually lead to decreased perfusion and stop the growth of the left ventricle.

What are the Signs & Symptoms of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome?
- Closing of the ductus arteriosus in a heart that is severely underdeveloped on the left results
in cyanosis and respiratory distress which can progress to cardiogenic shock and death.
- Co-occurring tricuspid regurgitation or right ventricular dysfunction can cause hepatomegaly to develop.
- On EKG, right axis deviation and right ventricular hypertrophy are common, but not indicative of HLHS. Chest x-ray may show a large heart (cardiomegaly) or increased pulmonary vasculature. Neonates with HLHS do not typically have a heart murmur, but in some cases, a pulmonary flow murmur or tricuspid regurgitation murmur may be audible.
- The first symptoms are cyanosis that does not respond to oxygen administration or poor feeding. Peripheral pulses may be weak and extremities cool to the touch. - HLHS often co-occurs with low birth weight and premature birth.
- In neonates with a small atrial septal defect, termed "restrictive", there is inadequate mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. These neonates quickly decompensate and develop acidosis and cyanosis.
- Co-occurring tricuspid regurgitation or right ventricular dysfunction can cause hepatomegaly to develop.
- On EKG, right axis deviation and right ventricular hypertrophy are common, but not indicative of HLHS. Chest x-ray may show a large heart (cardiomegaly) or increased pulmonary vasculature. Neonates with HLHS do not typically have a heart murmur, but in some cases, a pulmonary flow murmur or tricuspid regurgitation murmur may be audible.
- The first symptoms are cyanosis that does not respond to oxygen administration or poor feeding. Peripheral pulses may be weak and extremities cool to the touch. - HLHS often co-occurs with low birth weight and premature birth.
- In neonates with a small atrial septal defect, termed "restrictive", there is inadequate mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. These neonates quickly decompensate and develop acidosis and cyanosis.
HEART CONDITIONS Diseases and Treated FAQ's
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome can be diagnosed prenatally or after birth via echocardiography.
- Typical findings include a small left ventricle and aorta, abnormalities of the mitral and aortic valves, retrograde flow in the transverse arch of the aorta, and left-to-right flow between the atria.
- It is often recognized during the second trimester of pregnancy, between 18 and 24 weeks' gestation.
- Typical findings include a small left ventricle and aorta, abnormalities of the mitral and aortic valves, retrograde flow in the transverse arch of the aorta, and left-to-right flow between the atria.
- It is often recognized during the second trimester of pregnancy, between 18 and 24 weeks' gestation.
- Medical
Without life-prolonging interventions, HLHS is fatal, but with intervention, an infant may survive. A cardiothoracic surgeon may perform a series of operations or a full heart transplant.
While surgical intervention has emerged as the standard of care in the United States, other national health systems, notably in France, approach diagnosis of HLHS in a more conservative manner, with an emphasis on termination of pregnancy or compassionate care after delivery.
Before surgery, the ductus must be kept open to allow blood-flow using medication containing prostaglandin.
Air with less oxygen than normal is used for infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
These low oxygen levels increases the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) and thus improve blood flow to the rest of the body due to the greater pressure difference between the lungs and body. Achieving oxygen levels below atmosphere requires the use of inhaled nitrogen.
Nitric oxide is a potent pulmonary vasodilator, and thus reduces PVR and improves venous return.
Any factor that increases PVR will impede right sided flow.
Other Treatments according with the patient can be
- Surgical,
- Norwood Procedure,
- Hybrid Procedure,
- Glenn Procedure,
- Fontan Procedure and
- Fetal Surgery.
Without life-prolonging interventions, HLHS is fatal, but with intervention, an infant may survive. A cardiothoracic surgeon may perform a series of operations or a full heart transplant.
While surgical intervention has emerged as the standard of care in the United States, other national health systems, notably in France, approach diagnosis of HLHS in a more conservative manner, with an emphasis on termination of pregnancy or compassionate care after delivery.
Before surgery, the ductus must be kept open to allow blood-flow using medication containing prostaglandin.
Air with less oxygen than normal is used for infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
These low oxygen levels increases the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) and thus improve blood flow to the rest of the body due to the greater pressure difference between the lungs and body. Achieving oxygen levels below atmosphere requires the use of inhaled nitrogen.
Nitric oxide is a potent pulmonary vasodilator, and thus reduces PVR and improves venous return.
Any factor that increases PVR will impede right sided flow.
Other Treatments according with the patient can be
- Surgical,
- Norwood Procedure,
- Hybrid Procedure,
- Glenn Procedure,
- Fontan Procedure and
- Fetal Surgery.