Index
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
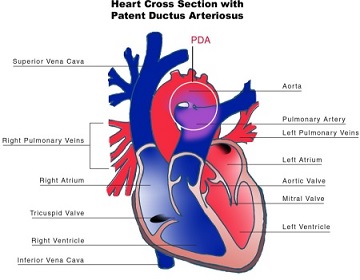
What Is Patent Ductus
Arteriosus (PDA)?
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth:
This allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta, which has a higher pressure, to the pulmonary artery.
Symptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter, but later in the first year of life there is often the onset of an increased work of breathing and failure to gain weight at a normal rate. With time, an uncorrected PDA usually leads to pulmonary hypertension followed by right-sided heart failure.
- The Ductus Arteriosus is a fetal blood vessel that normally closes soon after birth. In a PDA, the vessel does not close, but remains patent (open), resulting in an abnormal transmission of blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery. PDA is common in newborns with persistent respiratory problems such as hypoxia and has a high occurrence in premature newborns. Premature newborns are more likely to be hypoxic and have PDA due to underdevelopment of the heart and lungs.
- If transposition of the great vessels is present in addition to a PDA, the PDA is not surgically closed since it is the only way that oxygenated blood can mix with deoxygenated blood. In these cases, prostaglandins are used to keep the PDA open, and NSAIDs are not administered until surgical correction of the two defects is completed.
This allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta, which has a higher pressure, to the pulmonary artery.
Symptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter, but later in the first year of life there is often the onset of an increased work of breathing and failure to gain weight at a normal rate. With time, an uncorrected PDA usually leads to pulmonary hypertension followed by right-sided heart failure.
- The Ductus Arteriosus is a fetal blood vessel that normally closes soon after birth. In a PDA, the vessel does not close, but remains patent (open), resulting in an abnormal transmission of blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery. PDA is common in newborns with persistent respiratory problems such as hypoxia and has a high occurrence in premature newborns. Premature newborns are more likely to be hypoxic and have PDA due to underdevelopment of the heart and lungs.
- If transposition of the great vessels is present in addition to a PDA, the PDA is not surgically closed since it is the only way that oxygenated blood can mix with deoxygenated blood. In these cases, prostaglandins are used to keep the PDA open, and NSAIDs are not administered until surgical correction of the two defects is completed.
What Causes Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
PDA is more common in girls than boys. The condition is more common in premature infants and those with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Infants with genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, or babies whose mothers had rubella during pregnancy are at higher risk for PDA.
PDA is common in babies with congenital heart problems, such as hypoplastic left heart syndrome, transposition of the great vessels, and pulmonary stenosis.
Infants with genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, or babies whose mothers had rubella during pregnancy are at higher risk for PDA.
PDA is common in babies with congenital heart problems, such as hypoplastic left heart syndrome, transposition of the great vessels, and pulmonary stenosis.

What are the Signs & Symptoms of Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
Signs Include
- Left subclavicular thrill,
- Bounding pulse,
- Widened pulse pressure,
- Increased cardiac output,
- Increased systolic pressure,
- Patients typically present in good health, with normal respirations and heart rate.
If the PDA is moderate or large, widened pulse pressure and bounding peripheral pulses are frequently present, reflecting increased left ventricular stroke volume and diastolic run-off of blood into the (initially lower-resistance) pulmonary vascular bed. Prominent suprasternal and carotid pulsations may be noted secondary to increased left ventricular stroke volume,
- Tachycardia (a heart rate exceeding the normal resting rate),
- Continuous "machine-like" (also described as "rolling-thunder" and "to-and-fro") heart murmur (usually from aorta to pulmonary artery, with higher flow during systole and lower flow during diastole),
- Cardiomegaly (enlarged heart, reflecting ventricular dilation and volume overload),
- Poor growth,
- Differential cyanosis, (i.e. cyanosis of the lower extremities but not of the upper body.)
Common Symptoms Include
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath).
- Left subclavicular thrill,
- Bounding pulse,
- Widened pulse pressure,
- Increased cardiac output,
- Increased systolic pressure,
- Patients typically present in good health, with normal respirations and heart rate.
If the PDA is moderate or large, widened pulse pressure and bounding peripheral pulses are frequently present, reflecting increased left ventricular stroke volume and diastolic run-off of blood into the (initially lower-resistance) pulmonary vascular bed. Prominent suprasternal and carotid pulsations may be noted secondary to increased left ventricular stroke volume,
- Tachycardia (a heart rate exceeding the normal resting rate),
- Continuous "machine-like" (also described as "rolling-thunder" and "to-and-fro") heart murmur (usually from aorta to pulmonary artery, with higher flow during systole and lower flow during diastole),
- Cardiomegaly (enlarged heart, reflecting ventricular dilation and volume overload),
- Poor growth,
- Differential cyanosis, (i.e. cyanosis of the lower extremities but not of the upper body.)
Common Symptoms Include
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath).
HEART CONDITIONS Diseases and Treated FAQ's
PDA is usually diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Echocardiography
(in which sound waves are used to capture the motion of the heart) and associated Doppler
studies are the primary methods of detecting PDA. Electrocardiography (ECG),
in which electrodes are used to record the electrical activity of the heart, is not particularly
helpful as no specific rhythms or ECG patterns can be used to detect PDA.
A chest X-ray may be taken, which reveals overall heart size (as a reflection of the combined mass of the cardiac chambers) and the appearance of blood flow to the lungs. A small PDA most often accompanies a normal-sized heart and normal blood flow to the lungs. A large PDA generally accompanies an enlarged cardiac silhouette and increased blood flow to the lung.
As Prevention: Some evidence suggests that indomethacin administration on the first day of life to all preterm infants reduces the risk of developing a PDA and the complications associated with PDA. Indomethacin treatment in premature infants also may reduce the need for surgical intervention. .
A chest X-ray may be taken, which reveals overall heart size (as a reflection of the combined mass of the cardiac chambers) and the appearance of blood flow to the lungs. A small PDA most often accompanies a normal-sized heart and normal blood flow to the lungs. A large PDA generally accompanies an enlarged cardiac silhouette and increased blood flow to the lung.
As Prevention: Some evidence suggests that indomethacin administration on the first day of life to all preterm infants reduces the risk of developing a PDA and the complications associated with PDA. Indomethacin treatment in premature infants also may reduce the need for surgical intervention. .
- Neonates without adverse symptoms may simply be monitored as outpatients, while symptomatic PDA
can be treated with both surgical and non-surgical methods. Surgically, the DA may be closed by ligation
(though support in premature infants is mixed), either manually tied shut, or with intravascular coils or plugs
that leads to formation of a thrombus in the DA.
- Devices developed by Franz Freudenthal block the blood vessel with woven structures of nitinol wire.
- Because prostaglandin E2 is responsible for keeping the DA open, NSAIDs (which can inhibit prostaglandin synthesis) such as indomethacin or a special form of ibuprofen have been used to initiate PDA closure. Recent findings from a systematic review concluded that, for closure of a PDA in preterm and/or low birth weight infants, ibuprofen is as effective as indomethacin. It also causes fewer side effects (such as transient acute kidney injury) and reduces the risk of necrotising enterocolitis.
A review and meta-analysis showed that paracetamol may be effective for closure of a PDA in preterm infants.
A recent network meta-analysis that compared indomethacin, paracetamol and ibuprofen at different doses and administration schemes among them found that a high dose of oral ibuprofen may offer the highest likelihood of closure in preterm infants.
- While indomethacin can be used to close a PDA, some neonates require their PDA be kept open. Keeping a ductus arteriosus patent is indicated in neonates born with concurrent heart malformations, such as transposition of the great arteries.
Drugs such as alprostadil, a PGE-1 analog, can be used to keep a PDA open until the primary defect is corrected surgically.
- Devices developed by Franz Freudenthal block the blood vessel with woven structures of nitinol wire.
- Because prostaglandin E2 is responsible for keeping the DA open, NSAIDs (which can inhibit prostaglandin synthesis) such as indomethacin or a special form of ibuprofen have been used to initiate PDA closure. Recent findings from a systematic review concluded that, for closure of a PDA in preterm and/or low birth weight infants, ibuprofen is as effective as indomethacin. It also causes fewer side effects (such as transient acute kidney injury) and reduces the risk of necrotising enterocolitis.
A review and meta-analysis showed that paracetamol may be effective for closure of a PDA in preterm infants.
A recent network meta-analysis that compared indomethacin, paracetamol and ibuprofen at different doses and administration schemes among them found that a high dose of oral ibuprofen may offer the highest likelihood of closure in preterm infants.
- While indomethacin can be used to close a PDA, some neonates require their PDA be kept open. Keeping a ductus arteriosus patent is indicated in neonates born with concurrent heart malformations, such as transposition of the great arteries.
Drugs such as alprostadil, a PGE-1 analog, can be used to keep a PDA open until the primary defect is corrected surgically.
Known risk factors include:
- Preterm birth,
- Congenital rubella syndrome,
- Chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., Down syndrome),
- Genetic conditions such as Loeys–Dietz syndrome (would also present with other heart defects), Wiedemann–Steiner syndrome, and CHARGE syndrome.
- Preterm birth,
- Congenital rubella syndrome,
- Chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., Down syndrome),
- Genetic conditions such as Loeys–Dietz syndrome (would also present with other heart defects), Wiedemann–Steiner syndrome, and CHARGE syndrome.