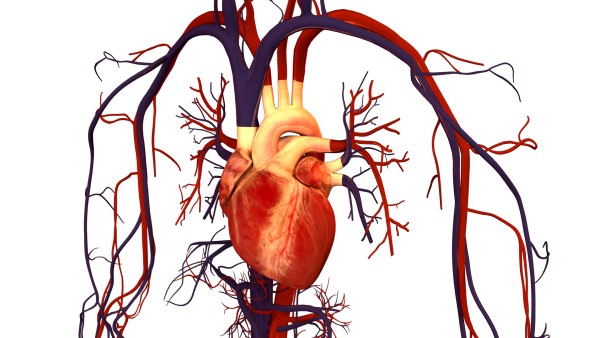
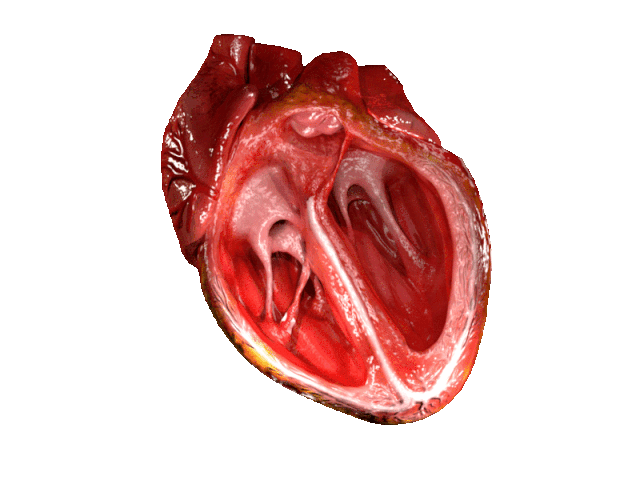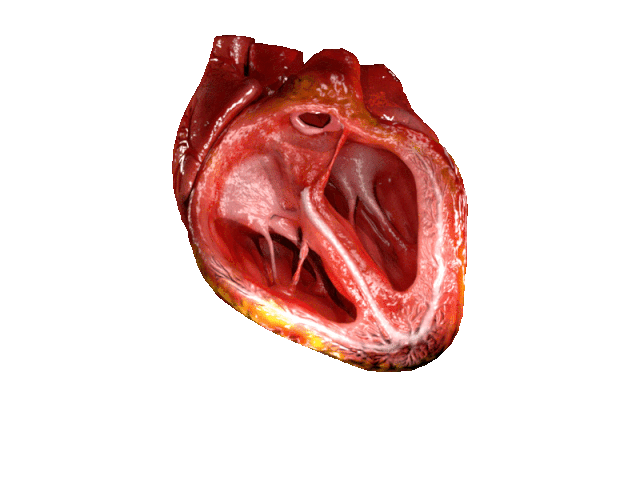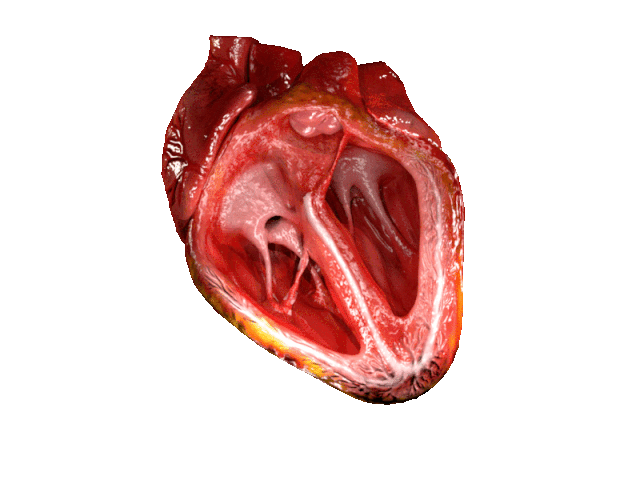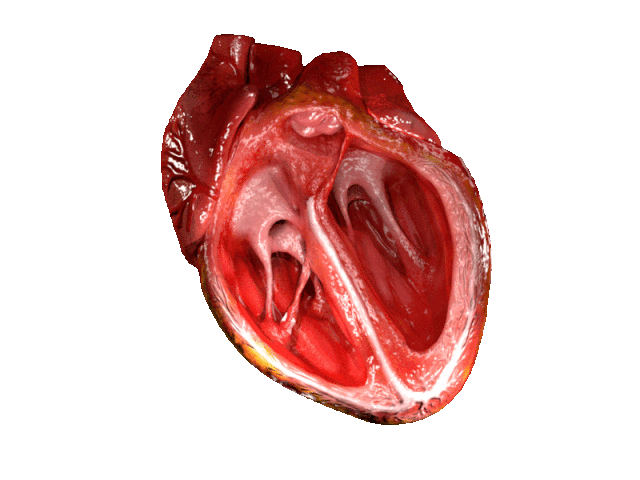
Cardiovascular surgeons operate on the heart and blood vessels to repair damage caused by diseases or disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Many times, a diagnosis of cardiovascular disease begins with the pediatric or primary care physician, who refers the patient to a cardiologist.
If the cardiologist decides that surgery is necessary, it will refer the patient to a cardiovascular surgeon, who becomes a new member of the
patient's cardiological team. (Even after the cardiac intervention, the patient remains under the care of the cardiologist.)
Cardiovascular surgeons perform many different types of operations, including valve repair and replacement, heart defect repair, coronary bypass,
aneurysm repair, laser trans-miocardial revascularization, and heart transplants. They also perform blood vessel operations, including the aorta
that is the body's main source of blood supply. Heart surgery today may also include the use or implantation of ventricular assist devices (DAVs),
mechanical devices that provide "assistance" to the underside heart, helping you pump blood throughout your body.
If your child needs surgery to repair a heart problem, a pediatric cardio surgeon (Heart Surgeon) has the knowledge and experience to treat your child.
Pediatric Cardiosurgeons offer the special care needed to correct congenital heart problems (Existing at Birth) and acquired in children.
Pediatric cardio surgeons treat complex congenital heart defects in newborns, children, and adolescents, as well as adults. Congenital heart defects
are very different from the types of heart disease that are common in adults. Repairing hearts in small bodies poses an additional challenge.
Pediatric Cardiosurgeons have special skills to provide the safest care, even for younger and younger patients who need heart surgery.
After surgery, the anesthesiology team monitors how the patient wakes up from anesthesia and monitors their postoperative progress.
 IMPORTANCE OF CARDIOLOGIST
IMPORTANCE OF CARDIOLOGIST PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY( Pathologies - Heart Disease and More )
PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY( Pathologies - Heart Disease and More ) WHAT IS THE ROLE OF CARDIOLOGIST.?MAIN TEST STUDIES OR TOP CARDIOLOGY TEST
WHAT IS THE ROLE OF CARDIOLOGIST.?MAIN TEST STUDIES OR TOP CARDIOLOGY TEST